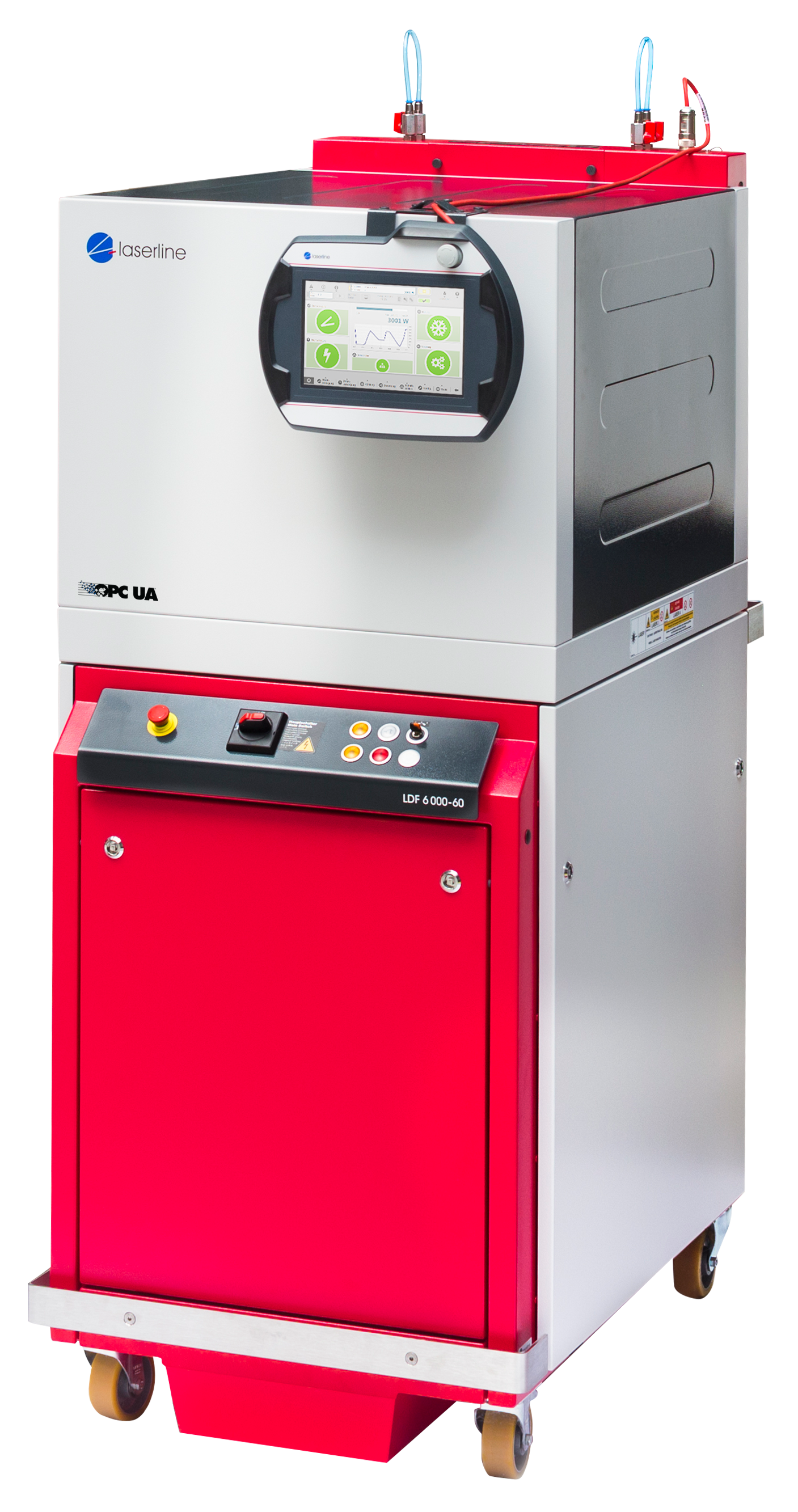
Diode lasers are used in various joining processes in industrial series production. High firmness and low distortion are the characteristics of laser welding involving our lasers. Plus, excellent seam surfaces can be achieved on the workpiece even at high cutting speeds. A distinction is made between heat conduction welding and keyhole welding.
Heat conduction welding with diode lasers is often used for workpieces with a low material thickness, such as thin sheets, foils, or wires. The laser beam is absorbed by the workpiece surface and the energy required is only led to the workpiece by heat conduction. The smooth, rounded welded seam that is created does not need to be post-processed. This method is suitable for the sheet metal working of materials such as stainless steel, for example, especially for manufacturing products that have to satisfy high requirements in terms of the visual quality of welded seams in the visible field.